Hydrogen, the most widespread atom in the universe, cannot claim to be a story in itself. The notoriety of this atom (or molecule: dihydrogen, H2, is commonly known as hydrogen) will exempt us from harping on about Captain Nemo’s vision of Jules Vernes’ Mysterious Island, or from plunging back into the debate on the advantages of lighter-than-air versus heavier-than-air for air transport (with its champion, Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin), or even from recalling more recent broken promises. And yet, with the announcement of the German, European and French plans (among others), it seems that with hydrogen, there is finally “something new in the state of energy”. On 17 February last, by ordinance, a new book (the 8th) was even dedicated to it in the French Energy Code. Is this new enthusiasm not rooted in the contrasting – even paradoxical – properties of hydrogen itself? Today, expectations are proportional to the resources announced (€7 billion for France alone). Success will certainly depend on a good mastery of these paradoxes.
Let’s go back over the main strategic plans around hydrogen
With the “Hulot” plan in 2018, France was the first to lay the foundations for the change of scale by setting out the objectives for 2020 in the PPE (Multiannual Energy Plan) decrees:
- Rate of decarbonized hydrogen in industrial hydrogen in 2023: 10% (~100.000t/year)
- Rate of decarbonized hydrogen in industrial hydrogen in 2028: 20% to 40% (~200,000 to 400,000t/year)
The announcement of the “National Strategy (Plan??) for the Development of Decarbonized Hydrogen in France” on 8/9/2020 not only confirmed the trajectory – 6.5GW of electrolysis in 2030 – but also budgeted financial resources: €7 billion including €3.4 billion for 2020-2023.
Finally, with the publication of the ordinance of 17/2/21 (which was provided for in the Climate Energy Law of 8/11/2019), a legal framework is being put in place; particularly by providing for a support mechanism for electrolysis production via calls for tenders (support in addition to remuneration and/or CAPEX).
Other European countries quickly followed suit by publishing ever more ambitious hydrogen plans, following the example of Germany in June 2020: 38 measures, €7 billion allocated to the promotion of hydrogen in Germany + €2 billion for international partnerships on hydrogen.
Obviously, at a European level, we are still changing scale: with the publication by the Commission on 8/7/2020 of “a hydrogen strategy for a climate-neutral Europe”, the objectives are moving towards:
- 6 GW electrolyser capacity by 2024
- 40 GW electrolyser capacity by2030
But hydrogen remains a paradoxical molecule
The high hopes of hydrogen for the transport sector (just like its too often postponed promises) are linked to its different energy density measurement: one of the highest densities per kg (more than 3 times the energy density of oil) but one of the lowest in volume (less than one third than that of natural gas), which obliges us to consider important compression levels – up to 750 bar – for mobility purposes.
Today, its most critical paradox lies in its impact on climate. Similar to electricity, hydrogen is a zero-emission energy carrier: its “combustion” only produces water. If the energy used for its production is clean, hydrogen will be clean (as is the case of hydrogen produced by electrolysis of water from renewable electricity). It is on this promise that the various hydrogen strategies have been developed as an essential technology for achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. But hydrogen can also achieve the worst carbon footprint per unit of energy: up to almost 1.5tCO2eq per MWh (in the case of electrolysis using coal-fired electricity).
At a European level, this risk does not seem to worry DG Clima which, looking ahead, is ready to deem as ‘clean’ any electricity drawn from the network since it will have to be clean in the long term. DG Comp, on the other hand, before approving the support mechanisms needed for the hydrogen sector (billions budgeted by the national plans) would like to know how to ensure at any given time that the H2 produced by electrolysis does indeed lead to the promised reduction in emissions.
No matter how boring this question may be, the credibility of the sector will depend on the quality of the answer.
An abundance of answers is currently under discussion: dedicated line / long term contract / PPAs / time correlation / geographical correlation, with renewable / low carbon / additional / subsidized / non-subsidized / certified by guarantees of origin / block-chain technology… and the sector is holding its breath waiting for clear rules.
In France, the electricity mix is already largely decarbonised, between the closure of the last coal-fired power plants scheduled for 2022, stable (or even decreasing) consumption and a Multiannual Energy Plan which foresees in its medium scenario more than 57 GW of additional solar and wind power capacity between 2019 and 2028. An “off-peak base ” operating mode (between 7500 and 8000 hours of annual operation and the capacity mechanism clearly indicates the hours to be avoided) should therefore satisfy the Commission.
In fact, if we extrapolate the monotone of solar + wind energy production in 2019 from this additional capacity, which represents more than 260% of the capacity in 2019, we obtain the following capacity values :
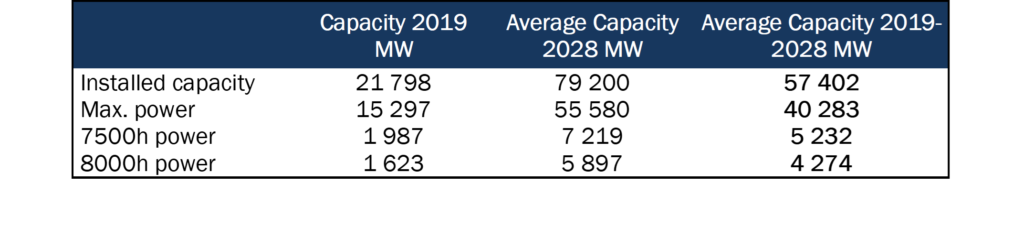
Thus, approx. 5GW of “new” renewable hydrogen will be available for nearly 8000 hours by 2028 and the 6.5GW planned for 2030 will also be able to claim the quality of renewable hydrogen.
The sector is waiting for the publication of the “Delegated Act” of the Directive on the promotion of renewable energies (RED 2) which must define the conditions under which hydrogen produced by electricity drawn from the network can be included in the national objectives for the share of renewable energies in the transport sector (objective of 14% by 2030). The publication of this Delegated Act by the European Commission is planned for the end of 2021 and is likely to set a precedent for the qualification of hydrogen produced by electrolysis, regardless of its final use. Therefore, it is not our intention to close the debate here, but rather hope that these projections will contribute to the current enthusiasm for the development of renewable and low-carbon hydrogen!
Philippe Boulanger







