Winter 2023/2024 has been a somewhat tense one. Both countries saw lower electricity prices compared to last winter, in line with increased market confidence following EU measures to counter the energy crisis. It should be noted that Spain experienced more price volatility than France this winter.
The French Market Analysis Winter 2022 vs Winter 2023
Winter 2022 and Winter 2023 in the French electricity market showcased distinct patterns in demand, generation sources, and market prices.
Demand:
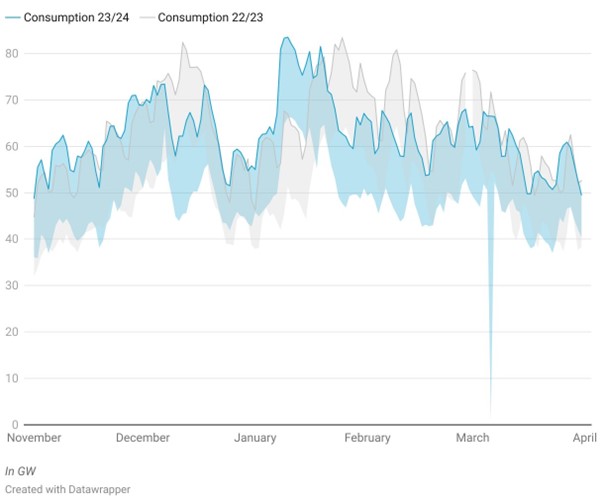
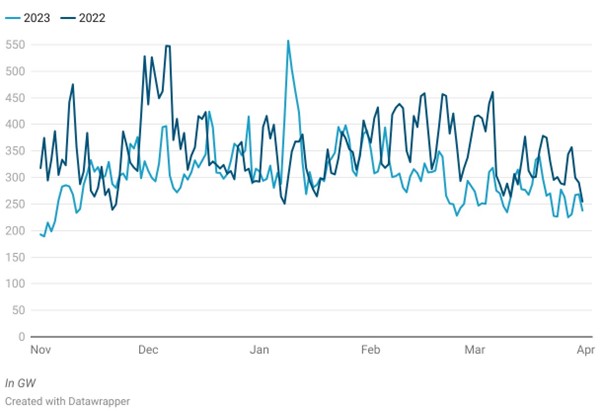
Winter 2022 started with an increase of demand in November due to colder weather, reaching an average of 57.1 GW, and peaked at 66.8 GW in December due to a cold spell, but lowered throughout December and into January as the weather proved mild. Demand rose again later in January and February due to colder weather before dropping again at the end of February.
In contrast, winter 2023 saw notable surges in demand throughout the first months of the season, with November witnessing a significant increase driven by higher peak consumption, followed by December peaking even higher at 73.4 GW despite mild winter forecasts. January 2024 maintained high demand levels, reaching 70.4 GW during normal periods and peaking at 83.5 GW. We saw a decrease in demand in February, averaging 62.3 GW, with a peak of 68 GW, while March saw a significant decline with peak periods averaging 57.9 GW.
Overall, while the beginning of winter 2023 saw significant peaks compared to winter 2022. Demand stabilized in the latter months due to milder weather. From February onward, power demand was significantly lower than last year, despite more affordable power prices.
Graphic 1: France Energy Consumption, Winter 2022 vs Winter 2023
Generation Impact on Demand:
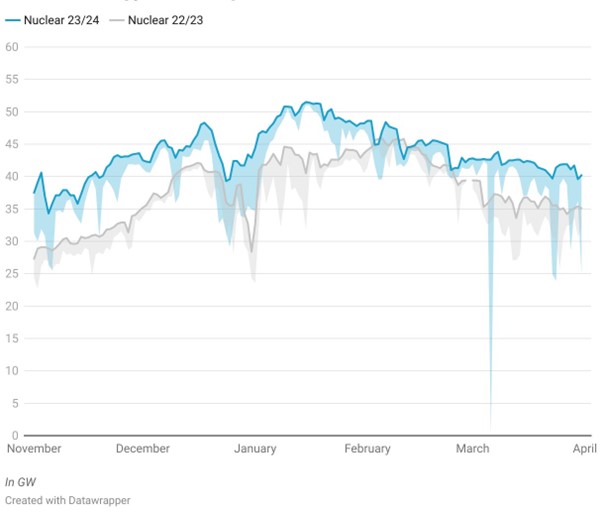
During winter 2022, high levels of demand were met through increased gas and coal generation, while renewables fluctuated throughout the winter period. The nuclear power supply remained low but stable due to maintenance in December. Driven by renewables’ decrease in production, gas power generation peaked in February. Nuclear in March varied significantly due to unavailabilities and strikes, while gas and coal generation decreased. Renewables, especially wind, played a more significant role in March.
Winter 2023 showed stability in nuclear and gas generation while seeing a decrease in coal usage. However, forecasts of nuclear generation from EdF consistently predicted greater generation throughout the season than the real generation, as anticipated by HES last year. Renewable energy played a significant role, especially wind power, which increased significantly, such as in December when it exceeded 20% of the mix. Overall, the winter 2023 generation mix rose in renewables and nuclear compared to last year, while gas remained relatively stable but low.
Graphic 2: France Nuclear Generation, Winter 2022 vs Winter 2023
Sources: RTE
Winter 2023/2024 Nuclear Generation: Actual vs RTE Prediction
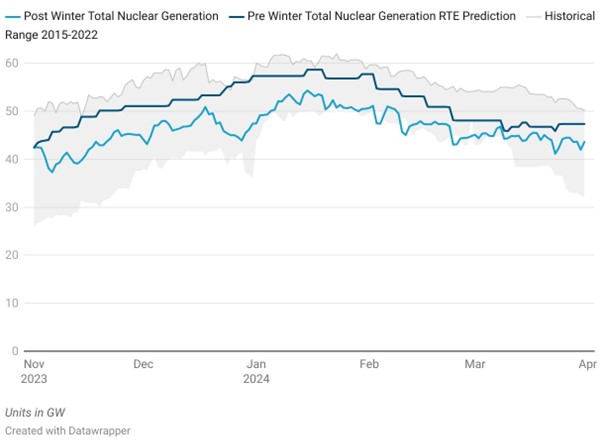
Source: RTE, HES
Market Prices:
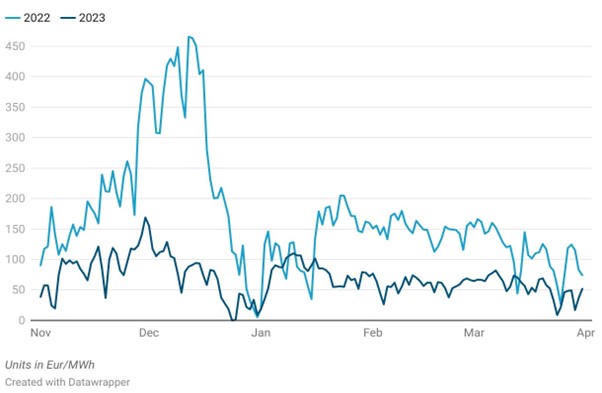
Winter 2022 witnessed large price fluctuations driven by gas supply uncertainties due to the invasion of Ukraine and ensuing sanctions in the later winter months, relatively limited installed power capacity available during peak demand periods, especially due to un-forecasted nuclear unavailabilities driven by corrosion issues. Gas contract prices fell due to full storage in November, while emissions prices rose with colder forecasts. Gas contract prices rose significantly already during the previous summer and, although they decreased subsequently at the beginning of winter, the overall high price levels remained leading to exceptionally high energy prices. This was exacerbated in February when the Ukraine invasion occurred, and gas prices skyrocketed.
By contrast, winter 2023, thanks to LNG supply chain networks and high storage levels saw lower gas prices and, consequently, also thanks to higher French nuclear availability, saw much lower electricity prices too.
Both periods highlight energy market complexities, with short-term fluctuations driven by immediate factors that we saw in the generation and demand section of this article and longer-term trends shaped by geopolitical concerns and sanctions coupled with nuclear plant maintenance concerns.
France Spot Electricity Price, Winter 2022 vs Winter 2023
Sources: EPEX
Overall, Winter 2023 showcased a significant increase in electricity demand, a notable surge in renewable energy contributions, and stability in nuclear and gas generation, leading to lower price levels. This is in contrast with the previous winter, which saw notable fluctuations in market prices driven by gas and emissions price dynamics, as well as the Ukraine war and a renewed push for renewables by the EU.
The Spanish Market Analysis Winter 2022 vs Winter 2023
Demand:
Winter 2022 saw the demand for electricity in Spain during November and December 2022 remained relatively stable, with slight fluctuations due to seasonal influences and weather conditions, although the price levels were overall high due to the energy crisis. January 2023 saw a surge in demand, driven by post-holiday activity. February saw improved stability and increased demand.
In Winter 2023, there was a notable rise in energy demand in November 2023, marking continued growth in electricity consumption. December 2023 also witnessed a significant increase, reinforcing the upward trajectory in electricity consumption. The increase in demand in Winter 2023 compared to Winter 2022 was primarily due to sustained economic activities post-holidays, colder temperatures, and continued economic growth, driving higher electricity consumption throughout the season, as well as lower power prices.
Generation Mix and Prices:
In the winter 2022 we saw increased wind power generation in November, which contributed to lower electricity prices. Hydro and solar generation varied in December, balancing renewables versus non-renewables at similar levels. Gas prices initially rose but fell sharply later, affected by EU gas contract caps and warmer temperatures, contributing to price drops along with falling gas prices and reduced CO2 costs. Wind, nuclear, and hydro remained the top generation sources in January, with renewables’ share rising to 56%.
Winter 2023 had even higher contributions from renewables, especially wind, and hydropower, which, together with successful EU-level energy crisis measures, led to reduced electricity prices despite fluctuations influenced by gas and CO2 contracts. Comparing the previous winter to this one, and taking into account the EU’s push this winter for decarbonization and COP24 as well as Spain’s reduction of nuclear generation, we can see that the fraction of renewables in the generation mix will likely continue to increase during the next winter. Currently, total generation is lower than the previous winter as Spain pivots toward renewables by decommissioning nuclear generation plants.
Spain Total Energy Generation, Winter 2022 vs Winter 2023
Sources: Entsoe
Gas and CO2 Prices:
In November 2022, gas prices initially fell but later rose, with CO2 prices also increasing. December saw gas prices initially rise but then fall sharply, while CO2 prices rose significantly. In January, gas prices dropped sharply due to ample supply, and CO2 futures fell slightly. In February, gas prices continued to fall, but CO2 futures rose notably. In March, gas prices decreased further, while CO2 contracts also decreased slightly. Overall, gas and CO2 prices in Winter 2022 showed fluctuations influenced by market dynamics, weather conditions, and regulatory factors.
In November 2023, Spain saw lower gas and CO2 prices, influencing electricity costs. December noted decreased gas prices and stable CO2 prices. January marked reduced gas and CO2 prices, stabilizing the energy market. February saw a further drop in gas prices and CO2 contracts, while March observed a slight increase in gas prices and CO2 contracts.
Comparing winter 2023 to winter 2022, gas and CO2 prices in winter 2023 generally showed a trend of decrease or stability, influenced by market dynamics and regulatory measures. This contrasts with Winter 2022, where gas and CO2 prices experienced more significant fluctuations and increases.
Regulatory and Policy Influences:
In the winter of 2022, the Spanish government aimed to stabilize electricity prices by integrating strategies into future contracts and tariffs, tackling price fluctuations, such as when the European Commission proposed a compromise on electricity market reform, favoring futures markets and long-term contracts. CO2 emission allowance price hikes affected electricity production costs, potentially due to regulatory changes or market dynamics. While efforts helped manage some fluctuations, market forces like gas price rises persisted.
Winter 2023 saw regulatory changes impacting gas and CO2 prices, notably lowering gas prices. Despite market dynamics, regulatory interventions, especially in CO2 and gas contracts, shaped market conditions and pricing trends significantly. These included EUETS regulations, which expanded to include methane and nitrous oxide emissions from large ships starting in 2026. Overall, Winter 2023 showed increased demand, significant renewable energy contributions, and lower gas and CO2 prices, emphasizing the transition to sustainable energy and the role of regulations in stabilizing markets.
Spain Spot Electricity Price, Winter 2022 vs Winter 2023
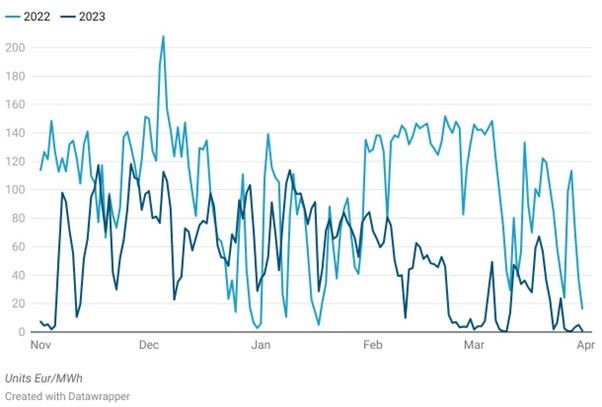
Sources: OMIE
Conclusions
Winter 2022/23 and 2023/24 were relatively unstable due to the Coronavirus pandemic, the invasion of Ukraine, and the French nuclear powerplant crisis. Comparing winter 2023/24 to winter 2022/23, we can see a stabilization in energy generation and prices across most of Europe. However, in coming years, with increased renewable energy and the decommissioning of several nuclear, coal, and gas power plants across Europe, power prices may fluctuate significantly and still strike high levels during peak demand periods. Meanwhile, the increase in installed renewable power capacity could also increase the frequency of zero-to-negative electricity prices. Therefore, the future energy markets will continue to have their share of uncertainties and fluctuations.
Spot Electricity Price Comparison France and Spain, Winter 2022 vs Winter 2023
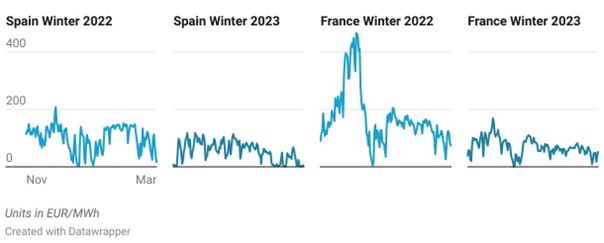
Source: OMIE; EPEX
Diego Marroquín González






